Title: Safeguarding Your Data: Understanding File System Security
Introduction:
In today’s digital landscape, where data breaches and cyber threats are a constant concern, ensuring the security of your files and sensitive information is paramount. File system security plays a crucial role in protecting your data from unauthorized access, manipulation, or loss. In this article, we will delve into the importance of file system security and explore essential measures to safeguard your valuable information.
Access Control:
One of the fundamental aspects of file system security is implementing robust access controls. By assigning permissions to users or groups, you can control who can read, write, or execute specific files or directories. Properly configuring access control lists (ACLs) helps maintain confidentiality and prevents unauthorized modification or deletion of critical files.
Encryption:
Encrypting sensitive files provides an additional layer of protection against unauthorized access. File-level encryption ensures that even if an attacker gains access to your data, they won’t be able to decipher its contents without the encryption key. Modern file systems often offer built-in encryption features or support third-party encryption tools that can be utilized to protect confidential information.
Regular Updates and Patches:
Keeping your file system up-to-date with the latest patches and updates is essential for maintaining security. Developers frequently release updates to address vulnerabilities discovered in file systems. By promptly applying these updates, you can mitigate potential risks and ensure that your file system remains resilient against emerging threats.
User Authentication:
Implementing strong user authentication mechanisms is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to your file system. Enforcing complex passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), or biometric authentication adds an extra layer of security by verifying the identity of users before granting them access to sensitive files.
Auditing and Monitoring:
Regularly auditing and monitoring your file system allows you to detect any suspicious activities or potential security breaches promptly. By implementing logging mechanisms and analyzing log data, you can identify unauthorized access attempts, unusual file modifications, or suspicious user behavior. These insights enable you to take proactive measures to mitigate security risks.
Backup and Disaster Recovery:
File system security is not just about preventing unauthorized access; it also involves protecting your data from accidental loss or hardware failures. Regularly backing up your files and having a robust disaster recovery plan in place ensures that you can recover your data in case of unforeseen events, such as ransomware attacks or system crashes.
Conclusion:
File system security is a critical component of safeguarding your valuable data from unauthorized access, manipulation, or loss. By implementing robust access controls, encryption, regular updates, user authentication mechanisms, auditing and monitoring practices, and backup solutions, you can significantly enhance the security of your file system. Remember that ensuring file system security is an ongoing process that requires continuous vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats. By prioritizing file system security measures, you are taking a proactive step towards protecting your sensitive information in today’s ever-connected digital world.
9 Essential Tips for Ensuring File System Security
- Use strong passwords and change them regularly.
- Securely back up your files on a regular basis.
- Use encryption to protect sensitive data stored on your file system.
- Keep your operating system and software up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Limit user access to only those who need it, and set appropriate permissions for each user or group of users.
- Utilize two-factor authentication whenever possible to ensure secure access to data stored in the file system, especially when accessed remotely or over the internet.
- Monitor activity within the file system for any suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts, such as unusual logins, failed login attempts, etc., and take corrective action immediately if necessary..
- Make sure all external storage devices are scanned for viruses before being connected to the network or accessing any files in the file system
- Disable AutoRun features that can be used by malicious software to gain unauthorized access into a computer’s file system
Use strong passwords and change them regularly.
Title: Strengthening File System Security: The Power of Strong Passwords
Introduction:
In the realm of file system security, one simple yet highly effective tip stands out: using strong passwords and changing them regularly. While it may seem like a basic practice, the impact of a strong password cannot be overstated. In this article, we will explore why strong passwords are vital for file system security and how regularly changing them can further fortify your defenses against potential threats.
The Importance of Strong Passwords:
A strong password acts as a robust barrier between your files and unauthorized access attempts. It should be unique, complex, and difficult to guess. By incorporating a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters, you create a password that is far more resilient to brute-force attacks or dictionary-based hacking attempts.
Avoid Common Pitfalls:
To ensure the strength of your password, it is essential to avoid common pitfalls. Steer clear of using easily guessable information such as names, birthdates, or repetitive patterns. Additionally, refrain from reusing passwords across multiple accounts or systems as this can increase the risk of compromise if one account is breached.
Regular Password Changes:
While creating a strong password is crucial, regular password changes add an extra layer of security. By periodically updating your passwords, you minimize the window of opportunity for potential attackers to gain unauthorized access to your file system. Aim to change your passwords every few months or as recommended by best practices in your industry.
Password Management Tools:
With the increasing number of online accounts and systems we use daily, managing multiple complex passwords can become challenging. Consider utilizing password management tools that securely store and generate strong passwords for you. These tools often have features like auto-fill capabilities that make logging into various systems effortless while ensuring each account has its unique and robust password.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
Complementing strong passwords with two-factor authentication (2FA) provides an additional layer of protection. 2FA requires users to provide a second form of verification, such as a code sent to their mobile device, in addition to entering their password. This added step significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password gets compromised.
Conclusion:
Using strong passwords and changing them regularly is a fundamental yet powerful practice for enhancing file system security. By incorporating complex combinations of characters, avoiding common pitfalls, and leveraging password management tools and 2FA, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your files. Remember that file system security is an ongoing effort, and reinforcing your defenses with strong passwords is an essential step towards safeguarding your valuable data in today’s digital landscape.
Securely back up your files on a regular basis.
Securely Back Up Your Files on a Regular Basis: A Vital File System Security Tip
One of the most crucial steps in ensuring file system security is securely backing up your files on a regular basis. Data loss can occur due to various reasons, including hardware failures, malware attacks, accidental deletions, or natural disasters. By implementing a robust backup strategy, you can protect your valuable files and ensure their availability even in the face of unexpected events.
Regular backups serve as a safety net, allowing you to recover your data quickly and minimize potential disruptions to your operations. Here are some key reasons why securely backing up your files is essential for file system security:
- Protection against Data Loss: Backing up your files regularly provides an extra layer of protection against data loss. In the event of hardware failures or accidental deletions, having a recent backup ensures that you can restore your files without significant downtime or loss of critical information.
- Defense against Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware attacks have become increasingly prevalent in recent years. These malicious programs encrypt your files and demand a ransom for their release. By maintaining secure backups stored separately from your primary file system, you can avoid falling victim to such attacks. Having access to clean backups allows you to restore your files without paying the ransom.
- Disaster Recovery Preparedness: Natural disasters such as fires, floods, or earthquakes can wreak havoc on your IT infrastructure. By regularly backing up your files and storing them off-site or in the cloud, you ensure that even if physical hardware is damaged or destroyed, you can recover your data and resume operations swiftly.
When implementing a secure backup strategy, consider the following best practices:
– Choose Reliable Backup Solutions: Select reputable backup software or services that offer encryption options and robust security measures to safeguard your data during transit and storage.
– Use Redundant Storage Locations: Store backups in multiple locations to mitigate risks associated with localized incidents like theft or localized disasters. This can include external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), or cloud storage services.
– Encrypt Your Backups: Encrypting your backups adds an extra layer of security, ensuring that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to your backup files, they cannot decipher the data without the encryption key.
– Test and Verify Your Backups: Regularly test and verify the integrity of your backups to ensure they are complete and can be restored successfully when needed. This helps avoid unpleasant surprises when attempting to recover files.
In conclusion, securely backing up your files on a regular basis is a vital tip for file system security. It provides protection against data loss, defends against ransomware attacks, and prepares you for disaster recovery scenarios. By following best practices and implementing a robust backup strategy, you can safeguard your valuable data and maintain business continuity even in the face of unforeseen events.
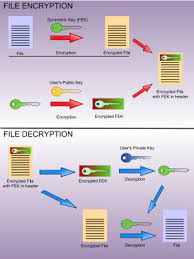
Use encryption to protect sensitive data stored on your file system.
Title: Enhancing File System Security: The Power of Encryption
In an era where data breaches and cyber threats are prevalent, protecting sensitive information has become a top priority for individuals and organizations alike. One effective measure to bolster file system security is the use of encryption. By encrypting sensitive data stored on your file system, you add an extra layer of protection that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Encryption is a process that transforms data into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms. This ensures that even if an unauthorized person gains access to your files, they won’t be able to decipher the content without the encryption key. Encryption provides confidentiality and integrity, making it a valuable tool in safeguarding sensitive information.
When implementing encryption for file system security, there are two primary types to consider: file-level encryption and full-disk encryption.
File-level encryption focuses on encrypting individual files or directories. This approach allows you to selectively encrypt specific files containing sensitive information while leaving other non-sensitive files untouched. It provides flexibility and granularity in protecting only those files that require heightened security.
Full-disk encryption, on the other hand, encrypts the entire disk or storage device where your file system resides. This means that all data stored on the disk is automatically encrypted, providing comprehensive protection against unauthorized access to any file within the system.
Modern operating systems often provide built-in encryption features or support third-party tools that facilitate easy implementation of both file-level and full-disk encryption. These tools employ strong cryptographic algorithms such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), ensuring robust security for your sensitive data.
It’s important to note that while encryption adds an extra layer of protection, it does not negate the need for other security measures such as access controls, user authentication, and regular updates. Implementing a multi-layered approach to file system security ensures comprehensive protection against various threats.
Furthermore, it’s crucial to manage and securely store encryption keys. Losing or compromising the encryption key could result in permanent data loss or render the encrypted files inaccessible. Therefore, it’s advisable to follow best practices for key management, such as securely storing keys separate from the encrypted data and regularly backing up encryption keys.
In conclusion, utilizing encryption is a powerful strategy to enhance file system security and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Whether you opt for file-level or full-disk encryption, implementing this security measure significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and ensures confidentiality. By combining encryption with other security practices, you can create a robust defense against potential threats and maintain the integrity of your valuable information in today’s digital landscape.
Keep your operating system and software up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates.
Title: The Key to File System Security: Keeping Your Software Updated
Introduction:
In the realm of file system security, one of the simplest yet most effective measures you can take is to ensure that your operating system and software are regularly updated with the latest security patches and updates. In this article, we will explore why this tip is crucial for maintaining a secure file system and protecting your valuable data.
The Importance of Updates:
Operating systems and software applications are constantly evolving, with developers working diligently to identify and fix vulnerabilities that could potentially be exploited by malicious actors. These vulnerabilities may allow unauthorized access, data breaches, or other security risks. By regularly updating your operating system and software, you can stay ahead of these threats and fortify your file system’s defenses.
Patch Vulnerabilities:
Security patches are released by software vendors to address known vulnerabilities in their products. These vulnerabilities could be discovered through internal testing or reported by users or security researchers. By promptly applying these patches, you close potential entry points that could be exploited by attackers. Neglecting updates increases the risk of falling victim to known exploits that have already been patched.
Stay Protected from Emerging Threats:
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, with new attack techniques emerging regularly. Hackers are continuously finding innovative ways to exploit weaknesses in operating systems and software applications. By keeping your software up-to-date, you benefit from the latest security enhancements developed specifically to counter these evolving threats. Regular updates ensure that your file system is equipped with the necessary defenses against emerging attack vectors.
Enhance Stability and Performance:
In addition to bolstering security, keeping your operating system and software updated also improves overall system stability and performance. Updates often include bug fixes, performance optimizations, and compatibility improvements that enhance the functionality of your file system. This ensures smooth operation while minimizing potential crashes or errors that could lead to data loss or corruption.
Automate Updates for Convenience:
To make the update process more convenient, many operating systems and software applications offer automatic update mechanisms. Enabling these features ensures that you receive the latest security patches and updates without manual intervention. By automating updates, you eliminate the risk of forgetting or delaying critical security measures, ensuring your file system remains secure at all times.
Conclusion:
Regularly updating your operating system and software with the latest security patches and updates is a vital step in maintaining a secure file system. It not only helps patch known vulnerabilities but also protects against emerging threats, enhances stability, and improves overall system performance. By prioritizing software updates, you are actively safeguarding your valuable data from potential security breaches in today’s ever-evolving digital landscape. Remember, staying proactive with updates is a key element of robust file system security.
Limit user access to only those who need it, and set appropriate permissions for each user or group of users.
Title: Restricting Access: A Crucial Step in File System Security
Introduction:
When it comes to file system security, limiting user access to only those who need it and setting appropriate permissions for each user or group is a fundamental practice. By implementing this simple yet effective tip, you can significantly enhance the security of your file system and protect your sensitive data from unauthorized access or accidental mishandling. In this article, we will explore why restricting user access is crucial and how to set appropriate permissions for optimal file system security.
Why Restrict User Access?
Granting unnecessary privileges to users can create potential vulnerabilities within your file system. Every user account represents a potential entry point for malicious actors or unintentional mistakes that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of your data. By limiting access to only those who genuinely require it, you minimize the risk of unauthorized actions and reduce the attack surface.
Setting Appropriate Permissions:
To ensure proper file system security, it’s essential to configure permissions appropriately for each user or group. Here are some key considerations:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Follow the principle of least privilege by granting users only the minimum level of access necessary to perform their specific tasks. Avoid giving blanket administrative privileges unless absolutely required.
- User Groups: Group users based on their roles and responsibilities within your organization. Assign permissions at the group level rather than individually whenever possible. This simplifies management and reduces the chances of overlooking individual accounts during permission reviews.
- Read/Write/Execute Permissions: Assign read, write, and execute permissions based on specific needs. Restrict write and execute permissions wherever possible to minimize accidental modifications or execution of malicious code.
- Regular Permission Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of user permissions to ensure they remain aligned with current requirements. Remove unnecessary access rights promptly when users change roles or leave the organization.
- Special Considerations: Be mindful of special considerations such as sensitive files or directories. Apply additional security measures, such as encryption or stricter access controls, to protect highly confidential data.
Conclusion:
Limiting user access to only those who need it and setting appropriate permissions for each user or group is a vital practice in file system security. By adhering to the principle of least privilege and regularly reviewing permissions, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, accidental data loss, or malicious activities within your file system. Implementing strong user access controls is a proactive step towards ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your valuable data. Remember, robust file system security requires a layered approach that combines multiple measures to create a comprehensive defense against threats.
Utilize two-factor authentication whenever possible to ensure secure access to data stored in the file system, especially when accessed remotely or over the internet.
Enhancing File System Security with Two-Factor Authentication
In an era where data breaches and cyber threats are on the rise, ensuring the security of your files and sensitive information is vital. One powerful tool that can significantly bolster file system security is two-factor authentication (2FA). By implementing 2FA, you add an extra layer of protection to your data, especially when accessing it remotely or over the internet.
Two-factor authentication goes beyond traditional password-based security measures by requiring users to provide two separate forms of identification before gaining access to their accounts or files. Typically, this involves combining something the user knows (such as a password) with something they possess (such as a unique code generated by a mobile app or received via SMS).
The beauty of 2FA lies in its ability to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access even if an attacker manages to obtain someone’s password. Even if a password is compromised through methods like phishing or brute-force attacks, the second factor acts as an additional barrier that prevents unauthorized entry into the file system.
When it comes to file system security, utilizing 2FA whenever possible is highly recommended, particularly for remote access scenarios. Remote access introduces additional vulnerabilities as data is transmitted over networks that may not be fully secure. By enabling 2FA, you ensure that even if someone intercepts login credentials during transmission, they won’t be able to gain access without the second authentication factor.
Implementing 2FA for file system access is relatively straightforward. Many file systems and cloud storage platforms offer built-in support for 2FA or integrate with third-party authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Authy. These apps generate time-sensitive codes that are required alongside a password during login attempts.
It’s important to note that while 2FA significantly enhances security, it should not be considered foolproof. It’s still essential to follow best practices such as using strong and unique passwords, regularly updating software and systems, and staying vigilant against social engineering attacks.
In conclusion, two-factor authentication is a powerful tool for securing access to data stored in file systems, especially when accessed remotely or over the internet. By requiring users to provide an additional authentication factor beyond passwords, 2FA adds an extra layer of protection that significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Implementing 2FA wherever possible strengthens file system security and helps safeguard your valuable data in an increasingly interconnected world.
Monitor activity within the file system for any suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts, such as unusual logins, failed login attempts, etc., and take corrective action immediately if necessary..
Title: Proactive Monitoring: Strengthening File System Security
In the realm of file system security, proactive monitoring is a vital practice to detect and respond to any suspicious activities or unauthorized access attempts promptly. By closely monitoring the activity within your file system, you can identify potential security breaches and take corrective action before they escalate into significant threats. This article explores the importance of monitoring file system activity and highlights its role in fortifying your overall security posture.
Monitoring activity within the file system involves keeping a vigilant eye on various indicators that may signal unauthorized access or suspicious behavior. These indicators can include unusual logins, failed login attempts, unexpected file modifications, or abnormal user behavior. By implementing robust monitoring mechanisms, you gain valuable insights into the activities occurring within your file system and can promptly address any potential security risks.
One of the primary benefits of proactive monitoring is early threat detection. By closely tracking user activity and analyzing log data, you can quickly identify signs of compromise or unauthorized access attempts. For instance, multiple failed login attempts from different IP addresses or unusual login times may indicate an ongoing brute-force attack. With timely detection, you can take immediate corrective action to mitigate the risk and prevent further damage.
Proactive monitoring also allows you to establish a baseline of normal behavior within your file system. By understanding what constitutes typical activities and usage patterns, any deviations from this baseline can be flagged as potentially suspicious. Anomalous behavior could include unexpected access to sensitive files or directories by users who typically have no reason to access them. By setting up alerts for such anomalies, you ensure that any unusual activity triggers an immediate response.
When it comes to taking corrective action based on monitored activities, speed is crucial. If suspicious behavior is detected or unauthorized access attempts are identified, it is imperative to respond swiftly to minimize potential damage or data loss. Depending on the severity of the situation, corrective actions may include terminating suspicious user sessions, revoking compromised credentials, or temporarily restricting access to affected files or directories. By promptly addressing security incidents, you can prevent further compromise and protect your valuable data.
In conclusion, proactive monitoring is a vital aspect of file system security. By actively monitoring file system activity for unusual behavior or unauthorized access attempts, you can detect potential threats early and take immediate corrective action. Regularly reviewing log data, setting up alerts for suspicious activities, and responding swiftly to security incidents are essential practices in maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of your data. By prioritizing proactive monitoring as part of your overall security strategy, you strengthen your defenses against evolving cyber threats and ensure the safety of your file system.
Make sure all external storage devices are scanned for viruses before being connected to the network or accessing any files in the file system
Title: Protecting Your Network: Scanning External Storage Devices for Viruses
In the digital age, where data is frequently shared and transferred across various devices, ensuring the security of your network and file system is crucial. One often overlooked but essential tip for maintaining file system security is to scan all external storage devices for viruses before connecting them to your network or accessing any files.
External storage devices, such as USB flash drives, external hard drives, or SD cards, are commonly used to transfer files between different systems. However, these devices can inadvertently introduce malware or viruses that can compromise the security of your network and files.
By scanning external storage devices for viruses before connecting them to your network or accessing any files, you minimize the risk of infecting your systems. Here’s why this practice is essential:
Preventing Virus Spread: Viruses can easily spread from infected external storage devices to your network and other connected devices. By scanning these devices beforehand, you can identify and remove any potential threats before they have a chance to infiltrate your systems.
Protecting Sensitive Data: External storage devices often carry important or sensitive data. Malware-infected files could compromise the confidentiality and integrity of this information. Scanning these devices ensures that no malicious software is introduced into your file system, safeguarding your sensitive data.
Safeguarding Network Resources: Viruses can consume valuable network resources by spreading rapidly or launching attacks on other connected systems. By scanning external storage devices, you reduce the risk of resource depletion caused by malware activities and maintain optimal network performance.
To effectively implement this tip on file system security:
Use Antivirus Software: Install reputable antivirus software on all computers connected to your network. Ensure that it is regularly updated with the latest virus definitions to effectively detect and eliminate potential threats.
Enable Automatic Scanning: Configure antivirus software to automatically scan external storage devices when they are connected to a computer. This proactive approach ensures that no infected files go undetected.
Educate Users: Educate all network users about the importance of scanning external storage devices before connecting them to the network or accessing files. Encourage them to be cautious when using such devices, especially if they have been used on other systems.
By incorporating this simple yet vital practice into your file system security routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections and protect your network from potential threats. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to ensuring a secure and resilient file system environment.
Disable AutoRun features that can be used by malicious software to gain unauthorized access into a computer’s file system
Title: Strengthening File System Security: Disabling AutoRun Features
In the realm of file system security, one often overlooked yet crucial measure is disabling AutoRun features. These features, although designed to enhance user convenience, can be exploited by malicious software to gain unauthorized access into a computer’s file system. By understanding and disabling AutoRun functionality, you can significantly reduce the risk of malware infiltration and fortify your overall system security.
AutoRun is a feature in operating systems that automatically executes specific actions when removable media (such as USB drives or CDs) are inserted into a computer. This feature was initially intended to simplify the process of launching applications or accessing files from external devices. However, it has become a favorite target for malware creators who exploit it to spread their malicious code.
Malicious software can take advantage of AutoRun by embedding itself within an autorun.inf file present on the removable media. When the infected media is connected to a computer with AutoRun enabled, the malware executes automatically without any user intervention. This allows unauthorized access to the file system and potentially leads to data breaches or system compromise.
To mitigate this risk, it is recommended to disable AutoRun functionality on your computer. Here’s how you can do it:
1. For Windows users:
– Open the Start menu and type “gpedit.msc” in the search bar.
– Select “Edit group policy” from the results.
– In the Group Policy Editor window, navigate to “Computer Configuration” > “Administrative Templates” > “Windows Components” > “AutoPlay Policies.”
– Double-click on “Turn off Autoplay.”
– Select “Enabled,” then choose “All drives” from the dropdown menu.
– Click “Apply” and then “OK.”
2. For macOS users:
– Go to the Apple menu and select “System Preferences.”
– Click on “CDs & DVDs.”
– Set the “When you insert a blank CD” and “When you insert a blank DVD” options to “Ignore.”
Disabling AutoRun reduces the risk of inadvertently executing malicious code from external media. However, it’s important to note that this measure should be accompanied by other security practices such as using reputable antivirus software, keeping your operating system and applications up to date, and exercising caution when connecting unknown or suspicious devices.
By taking the proactive step of disabling AutoRun features, you are strengthening your file system security and minimizing the potential for unauthorized access. This simple yet effective measure adds an extra layer of protection against malware and contributes to a more secure computing environment. Stay vigilant, stay secure!
