Storage Virtualization: Unleashing the Power of Data Efficiency
In today’s digital age, where data is growing exponentially, businesses face the challenge of managing and optimizing their storage infrastructure. This is where storage virtualization comes into play, revolutionizing the way organizations store and access their valuable information.
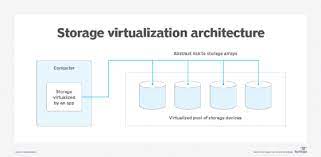
So, what exactly is storage virtualization? It refers to the abstraction of physical storage resources into a virtualized pool that can be easily managed and allocated as needed. By decoupling the logical view of data from its physical location, storage virtualization enables greater flexibility, scalability, and efficiency in handling storage resources.
One of the key benefits of storage virtualization is its ability to simplify management. With traditional storage systems, each device typically requires separate configuration and management processes. However, with virtualization, administrators can centrally manage multiple storage devices through a single interface. This streamlines operations, reduces administrative overheads, and allows for more efficient resource allocation.
Furthermore, storage virtualization improves utilization rates by pooling together disparate storage devices. Instead of having isolated islands of underutilized capacity across various systems, organizations can consolidate their resources into a shared pool. This not only optimizes space utilization but also eliminates the need for overprovisioning individual devices.
Another advantage is enhanced data mobility. With traditional storage setups, moving data between different systems or upgrading hardware often involves complex and time-consuming processes. Storage virtualization simplifies this by enabling seamless migration and data movement between different physical devices within the virtualized environment. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing needs without disrupting operations or incurring significant downtime.
Data protection is also strengthened through storage virtualization. By implementing features like snapshots and replication at the virtual layer, organizations can create efficient backup and disaster recovery solutions. These capabilities provide an added layer of security against data loss or system failures while minimizing recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO).
Moreover, storage virtualization aligns well with cloud computing and hybrid infrastructure models. It provides a foundation for building scalable and flexible storage solutions that can seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms. This enables organizations to leverage the benefits of cloud storage, such as elasticity and cost optimization, while maintaining control over their data.
However, it’s important to note that implementing storage virtualization requires careful planning and consideration. Organizations must evaluate their specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and compatibility with virtualization technologies. Additionally, proper data management practices and monitoring mechanisms should be in place to ensure optimal performance and security.
In conclusion, storage virtualization represents a significant advancement in the realm of data storage and management. By abstracting physical resources into a virtualized pool, businesses can unlock greater efficiency, flexibility, and scalability. With simplified management processes, improved resource utilization, enhanced data mobility, and strengthened data protection capabilities, storage virtualization empowers organizations to navigate the ever-growing demands of the digital landscape with ease. Embracing this technology can be a game-changer for businesses seeking to optimize their storage infrastructure while staying ahead in the competitive market.
Commonly Asked Questions About Storage Virtualization: Types, Meaning, Differences, and Google Drive
- What are the 3 types of virtualization?
- What is meant by storage virtualization?
- How is storage virtualization different from software virtualization?
- Is Google Drive storage virtualization?
What are the 3 types of virtualization?
The three types of virtualization commonly referred to in the technology industry are:
- Server Virtualization: Server virtualization involves partitioning a physical server into multiple virtual machines (VMs), each running its own operating system and applications. This allows for better utilization of hardware resources by consolidating multiple servers onto a single physical machine. Server virtualization offers benefits such as improved server efficiency, reduced hardware costs, simplified management, and increased flexibility in deploying and scaling applications.
- Network Virtualization: Network virtualization abstracts the traditional network infrastructure by creating logical networks that are decoupled from the underlying physical network hardware. This enables the creation of multiple virtual networks or segments on a shared physical network infrastructure. Network virtualization enhances flexibility and agility by allowing network administrators to provision, manage, and secure networks more efficiently. It also enables the implementation of advanced networking features such as load balancing, firewalls, and routing without requiring changes to physical network components.
- Storage Virtualization: Storage virtualization abstracts physical storage resources from their underlying hardware, creating a unified pool of storage that can be centrally managed and allocated as needed. It allows for greater flexibility in managing storage capacity, simplifies data migration and replication processes, improves data protection through features like snapshots and replication, and optimizes resource utilization by pooling together disparate storage devices.
These three types of virtualization—server, network, and storage—play crucial roles in modern IT infrastructure management by providing organizations with increased efficiency, scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. They form the foundation for building dynamic and agile environments that can adapt to changing business needs while maximizing resource utilization.
What is meant by storage virtualization?
Storage virtualization refers to the process of abstracting physical storage resources, such as hard drives, solid-state drives, or storage area network (SAN) devices, into a virtualized pool. It involves separating the logical view of data from its underlying physical storage infrastructure.
In simpler terms, storage virtualization allows multiple storage devices to be combined and managed as a single, unified resource. This virtualization layer sits between the applications or operating systems that require storage and the physical storage devices themselves.
By decoupling the logical representation of data from the physical hardware, storage virtualization provides several benefits. It simplifies management by centralizing control and administration of multiple storage devices through a single interface. It also improves resource utilization by pooling together disparate storage resources, eliminating isolated islands of underutilized capacity.
Additionally, storage virtualization enables greater flexibility and scalability. Data can be easily moved or migrated between different physical devices within the virtualized environment without disrupting operations. This agility allows organizations to adapt to changing needs more efficiently.
Moreover, storage virtualization enhances data protection and disaster recovery capabilities. Features like snapshots and replication can be implemented at the virtual layer to create efficient backup solutions and facilitate faster recovery in case of data loss or system failures.
Storage virtualization can be implemented using various technologies such as software-defined storage (SDS), hypervisors, or specialized hardware appliances. These technologies provide the necessary abstraction layer and management tools to create a unified view of storage resources.
Overall, storage virtualization empowers organizations with greater control over their data infrastructure while optimizing resource utilization, simplifying management tasks, and improving data mobility and protection.
How is storage virtualization different from software virtualization?
While both storage virtualization and software virtualization involve the concept of abstraction and virtualization, they are distinct in terms of their focus and purpose.
Storage virtualization primarily deals with abstracting and pooling physical storage resources to create a logical layer that simplifies management, enhances scalability, and improves resource utilization. It enables centralized management of multiple storage devices through a single interface, allowing for efficient allocation and optimization of storage capacity. Storage virtualization focuses on the efficient handling of data storage resources.
On the other hand, software virtualization is concerned with abstracting and isolating software applications or operating systems from the underlying hardware infrastructure. It allows multiple software instances or environments to run independently on a single physical server or machine. Software virtualization creates a layer of abstraction between the hardware and software, enabling greater flexibility, portability, and resource optimization for applications.
In summary, while storage virtualization is specifically related to managing storage resources effectively by abstracting physical devices into a virtualized pool, software virtualization pertains to abstracting software applications or operating systems from the underlying hardware infrastructure to enable better utilization and flexibility. Both forms of virtualization offer significant benefits in their respective domains but address different aspects of IT infrastructure optimization.
Is Google Drive storage virtualization?
Yes, Google Drive can be considered a form of storage virtualization. Google Drive is a cloud-based storage service that allows users to store, access, and manage their files and documents online. It abstracts the physical storage infrastructure by providing a virtualized pool of storage resources accessible over the internet.
When you upload files to Google Drive, they are stored on Google’s servers, which are part of a vast distributed storage infrastructure. However, as a user, you don’t need to worry about the physical location or management of those servers. Instead, you interact with your files through a virtual interface provided by the Google Drive platform.
Google Drive offers features like file synchronization across devices, file sharing and collaboration capabilities, version control, and integration with other Google services. These features are made possible through the underlying storage virtualization technology that allows for seamless access and management of files from various devices and locations.
By utilizing storage virtualization techniques, Google Drive provides users with the ability to access their files from anywhere with an internet connection while abstracting the complexities of managing physical storage infrastructure. This enables users to focus on their data and productivity rather than dealing with hardware maintenance or capacity limitations.
Overall, Google Drive exemplifies how storage virtualization can simplify file management and enhance accessibility in today’s digital world.
