File System Software: Simplifying Data Storage and Management
In the realm of information technology, file system software plays a crucial role in organizing, storing, and retrieving data efficiently. It serves as the backbone of modern computing systems, enabling users to manage files and directories seamlessly. From personal computers to massive data centers, file system software is a fundamental component that ensures data integrity and accessibility.
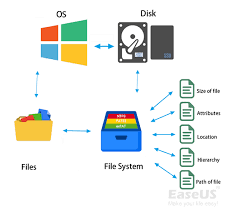
At its core, file system software is responsible for managing how data is stored on storage devices such as hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), or network-attached storage (NAS) systems. It provides a logical structure that allows users to organize files into directories or folders for easy navigation. Additionally, it handles file naming conventions, permissions, and access control to protect sensitive information.
One of the key features of file system software is its ability to allocate disk space efficiently. It ensures that files are stored in contiguous blocks whenever possible to minimize fragmentation and optimize read/write operations. This results in faster access times and improved overall performance.
Another important aspect of file system software is its support for various file types and formats. Whether it’s documents, images, videos, or application files, the software must be able to handle different data types seamlessly. This versatility enables users to work with diverse sets of information without compatibility issues.
Moreover, file system software often incorporates advanced features like compression and encryption. Compression algorithms reduce the size of files without compromising their integrity, saving valuable storage space. Encryption algorithms provide an additional layer of security by encoding files so that only authorized individuals can access them.
In recent years, with the rise of cloud computing and distributed storage systems, file system software has evolved to cater to these new paradigms. Distributed file systems enable seamless sharing and collaboration across multiple devices or locations by replicating data across servers or nodes in a network. This allows for high availability and fault tolerance while maintaining data consistency.
Furthermore, modern file system software often integrates with backup and recovery solutions. It enables users to create automated backups of their data, ensuring that critical information is protected from accidental loss or hardware failures. These features provide peace of mind and help organizations maintain business continuity.
As technology continues to advance, file system software is adapting to meet the demands of emerging trends such as big data, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT). These new frontiers require robust file systems capable of handling massive amounts of data, processing it efficiently, and ensuring its integrity.
In conclusion, file system software is an integral part of today’s digital landscape. It simplifies data storage and management by providing a structured approach to organizing files while optimizing performance and security. As technology evolves, file system software will continue to evolve alongside it, empowering users with efficient data handling capabilities in an increasingly complex digital world.
Commonly Asked Questions About File System Software
- What file system does my computer use?
- What is the best example of file systems?
- Is file system still used?
- What is file system software?
What file system does my computer use?
To determine the file system used by your computer, you can follow these steps:
Windows:
– Open File Explorer by pressing the Windows key + E.
– Right-click on the drive you want to check (e.g., C: or D:) and select “Properties”.
– In the General tab, under “File System”, you will see the type of file system used.
macOS:
– Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner and select “About This Mac”.
– In the Overview tab, click on “Storage”.
– You will see a visual representation of your storage devices. Click on each device to see its file system type.
Linux:
– Open a terminal window.
– Type the command `df -T` and press Enter.
– The output will display a list of mounted file systems along with their corresponding types.
Common file systems used in different operating systems are:
– Windows: NTFS (New Technology File System) is commonly used for internal drives, while exFAT or FAT32 may be used for external drives.
– macOS: macOS typically uses APFS (Apple File System) for newer versions, while HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus) is still in use for older versions.
– Linux: Various file systems like ext4, XFS, and Btrfs are commonly used depending on the distribution and user preference.
By following these steps, you can easily identify the file system employed by your computer’s drives.
What is the best example of file systems?
There are several notable file systems that have made significant contributions to the field of data storage and management. Here are some examples:
- File Allocation Table (FAT): FAT is a file system developed by Microsoft and widely used in early personal computers, external storage devices, and removable media. It is known for its simplicity, compatibility across different operating systems, and support for small to medium-sized storage capacities.
- NTFS (New Technology File System): NTFS is a proprietary file system developed by Microsoft for their Windows operating systems. It offers advanced features such as file compression, encryption, access control lists (ACLs), and support for large storage capacities. NTFS has become the default file system for Windows-based computers.
- HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus): HFS+ is a file system developed by Apple Inc. It was introduced with Mac OS 8.1 and has been the standard file system for macOS until the introduction of APFS (Apple File System). HFS+ supports features like journaling, metadata indexing, case-insensitive or case-sensitive file naming options, and support for large files and volumes.
- ext4: ext4 is a widely used open-source file system in Linux-based operating systems. It is an evolution of the earlier ext3 file system and offers improvements in performance, scalability, and reliability. ext4 supports larger file sizes and volumes compared to its predecessor.
- ZFS (Zettabyte File System): ZFS is an advanced open-source file system developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle). It provides features like data integrity checks, automatic repair capabilities, snapshots for efficient backups, RAID-like functionality called “ZFS pools,” and flexible storage allocation.
- APFS (Apple File System): APFS is a modern file system introduced by Apple Inc., replacing HFS+ as the default on macOS High Sierra and later versions. APFS offers enhanced performance, improved data integrity, support for encryption, snapshots, and efficient storage allocation. It is specifically designed for solid-state drives (SSDs) and flash-based storage.
These examples represent a range of file systems with different strengths and use cases. The “best” file system depends on factors such as the intended platform or operating system, specific requirements (e.g., performance, security), and the scale of storage needs.
Is file system still used?
Absolutely! File systems are still widely used and continue to be a fundamental component of modern computing systems. Despite the rise of cloud storage and distributed file systems, traditional file systems remain essential for various applications and environments.
On personal computers and laptops, file systems like NTFS (New Technology File System) for Windows or HFS+ (Hierarchical File System Plus) for macOS are the backbone of organizing and managing files. These file systems provide the necessary structure to store documents, images, videos, and other user data.
In enterprise environments, file systems play a crucial role in managing large-scale data storage solutions. Network-attached storage (NAS) devices utilize file systems such as ZFS (Zettabyte File System) or ext4 to enable efficient sharing of files across networks. These file systems offer advanced features like data deduplication, snapshots, and RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations for enhanced reliability and performance.
File systems also have a significant presence in server environments. They facilitate storing and retrieving data on hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs) within servers or data centers. Common server file system examples include ext4, XFS (eXtended File System), or Btrfs (B-Tree File System). These file systems are designed to handle high volumes of data with optimized performance characteristics.
Moreover, embedded devices like smartphones, tablets, cameras, and IoT devices rely on file systems to organize their internal storage. Mobile operating systems such as Android or iOS utilize specific file system formats like F2FS (Flash-Friendly File System) or APFS (Apple File System).
While cloud storage platforms often abstract away the underlying file system complexities from end-users, they still rely on robust file system software behind the scenes. Distributed file systems like Google Cloud Storage’s Colossus or Amazon S3’s object storage employ advanced techniques for scalability, fault tolerance, and data consistency.
In summary, file systems continue to be an integral part of the digital landscape, serving as the foundation for organizing, managing, and accessing data across a wide range of devices and environments. They provide the necessary structure and features to ensure efficient data storage, retrieval, and protection.
What is file system software?
File system software, also known as a file system or file management system, is a critical component of operating systems and storage devices. It provides the necessary infrastructure to organize, store, retrieve, and manage files and directories on storage media such as hard drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), or network-attached storage (NAS) systems.
At its core, file system software establishes a logical structure that allows users to create directories or folders to organize their files. This hierarchical organization simplifies navigation and helps users locate specific files efficiently. Additionally, file system software manages file naming conventions and supports various file types and formats.
One of the primary functions of file system software is disk space management. It allocates space on storage devices to store files in a structured manner. It aims to minimize fragmentation by storing files in contiguous blocks whenever possible. By doing so, it optimizes read/write operations and enhances overall performance.
File system software also handles access control and permissions for files and directories. It ensures that only authorized users can access specific files based on assigned permissions. This helps protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or modifications.
Moreover, file system software often incorporates additional features such as compression and encryption. Compression algorithms reduce the size of files without sacrificing their integrity, saving valuable storage space. Encryption algorithms encode files with mathematical algorithms to make them unreadable without proper decryption keys, providing an extra layer of security for sensitive data.
In recent years, with the advent of cloud computing and distributed storage systems, file system software has evolved to support these new paradigms. Distributed file systems enable seamless sharing and collaboration across multiple devices or locations by replicating data across servers or nodes in a network. This allows for high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability while maintaining data consistency.
Overall, file system software plays a vital role in managing data on various storage devices in an efficient and organized manner. It ensures that files are accessible when needed while maintaining data integrity and security. As technology advances, file system software continues to evolve to meet the demands of emerging trends and storage technologies.
