File System Security Protocols: Safeguarding Your Data
In today’s digital age, where data is the lifeblood of organizations, ensuring the security of file systems has become paramount. File system security protocols play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, tampering, or loss. In this article, we will explore the importance of file system security protocols and highlight some common practices to protect your valuable data.
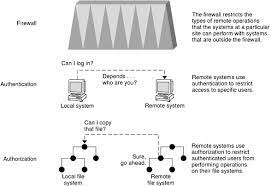
File system security protocols encompass a range of measures designed to establish access controls, encryption, auditing, and integrity checks within a file system. These protocols work in tandem to create multiple layers of defense against potential threats. Let’s delve into some key aspects:
- Access Controls: Implementing robust access controls is essential to limit who can access specific files or directories within a file system. Access control lists (ACLs) and role-based access control (RBAC) are commonly used mechanisms for defining and enforcing permissions. By granting appropriate privileges only to authorized users or groups, you can minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Encryption: File system encryption ensures that data remains protected even if it falls into the wrong hands. Encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) can be applied at various levels – full disk encryption (FDE), file-level encryption, or even individual data blocks within files. This adds an extra layer of security by rendering data unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
- Auditing and Logging: Logging activities within a file system provides an audit trail that helps track user actions and detect any suspicious activities or breaches. By enabling logging features, administrators can monitor file accesses, modifications, deletions, and other critical events that may indicate potential security incidents.
- Integrity Checks: Integrity checks ensure that files remain unaltered and free from unauthorized modifications or corruption. Hash functions such as SHA-256 can generate unique signatures for each file or block of data. Regularly verifying these signatures against the original ones helps detect any unauthorized changes.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: While not strictly a security protocol, having robust backup and disaster recovery mechanisms in place is vital for file system security. Regularly backing up data ensures that even if files are compromised or lost, they can be restored from a secure backup source.
Implementing these file system security protocols requires a comprehensive approach that combines technical measures, user awareness, and organizational policies. Here are some best practices to consider:
– Regularly patch and update your file system software to address any known vulnerabilities.
– Enforce strong password policies and two-factor authentication for accessing file systems.
– Train users on secure data handling practices, such as avoiding suspicious email attachments or sharing sensitive information through insecure channels.
– Conduct periodic security audits to identify vulnerabilities and potential weaknesses in your file system infrastructure.
– Employ intrusion detection systems (IDS) or intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to actively monitor network traffic for any signs of unauthorized access attempts.
Remember that file system security is an ongoing process. As technology advances and new threats emerge, it’s crucial to stay vigilant and adapt your security protocols accordingly.
In conclusion, file system security protocols are essential for protecting valuable data from unauthorized access, tampering, or loss. By implementing access controls, encryption mechanisms, auditing/logging features, integrity checks, and robust backup strategies, organizations can establish a strong defense against potential threats. Invest in the right combination of technical measures and user awareness to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your data within the file system.
Enhancing File System Security: 5 Essential Tips for Protecting Your Data
- Use strong passwords
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Regularly update software
- Monitor activity
- Backup frequently
Use strong passwords
One of the simplest yet most effective tips for enhancing file system security protocols is to use strong passwords. Passwords act as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to files and data. Unfortunately, many people still underestimate the importance of using strong, unique passwords.
A strong password is one that is difficult for others to guess or crack through automated methods. Here are some key considerations when creating a strong password:
- Length: Opt for longer passwords as they are generally harder to crack. Aim for a minimum of 12 characters, but the longer, the better.
- Complexity: Include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters in your password. This adds complexity and further increases its strength.
- Avoid Personal Information: Refrain from using easily guessable information such as your name, birthdate, or address in your password. Hackers can easily obtain this information through social engineering or data breaches.
- Unique Passwords: Use different passwords for each online account or system you access. Reusing passwords across multiple accounts increases the risk of compromise if one account is breached.
- Avoid Common Patterns: Steer clear of common patterns like sequential numbers (123456) or repeated characters (aaaaaa). These patterns are easily guessed by attackers using automated tools.
- Consider Passphrases: Instead of relying on a single word, consider creating a passphrase by combining multiple words with spaces or special characters between them. Passphrases are easier to remember while still providing increased complexity.
Remember, even with a strong password, it’s important to practice good password hygiene:
– Change your passwords periodically.
– Never share your passwords with anyone.
– Use two-factor authentication whenever possible.
– Be cautious when entering your password on shared or public computers.
– Regularly monitor for any suspicious activity related to your accounts.
By following these guidelines and adopting strong password practices, you can significantly enhance the security of your file system. Remember, the effort you put into creating and maintaining strong passwords is a small investment that can go a long way in protecting your valuable data from unauthorized access.
Enable two-factor authentication
Enhancing File System Security: The Power of Two-Factor Authentication
In the realm of file system security protocols, one simple yet highly effective measure stands out: enabling two-factor authentication (2FA). This additional layer of security provides an extra barrier against unauthorized access and significantly strengthens the overall protection of your sensitive data.
Two-factor authentication is a method that requires users to provide two separate forms of identification before gaining access to a system or application. Typically, it combines something the user knows (such as a password or PIN) with something they possess (such as a physical device or mobile phone).
By implementing 2FA for file system access, you add an additional step that goes beyond relying solely on a password. Even if someone manages to obtain or guess your password, they would still need the second factor (usually a unique code generated by an authentication app or received via SMS) to gain entry. This greatly reduces the risk of unauthorized individuals infiltrating your file system.
Enabling 2FA is relatively straightforward. Many file system platforms and applications offer built-in support for this security feature. Users can link their accounts with an authenticator app like Google Authenticator or receive one-time codes via SMS. Once set up, each login attempt will require not only a password but also the second factor for successful authentication.
The benefits of enabling two-factor authentication are numerous:
- Enhanced Security: By adding an extra layer of verification, 2FA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access to your file system. Even if passwords are compromised, hackers would still need physical possession of the second factor to gain entry.
- Protection against Password Weaknesses: Many security breaches occur due to weak passwords or password reuse across multiple platforms. With 2FA in place, even if a weak password is used, unauthorized access is unlikely without possession of the second factor.
- User Accountability: Two-factor authentication promotes accountability among users by ensuring that each login attempt is tied to a specific individual. This makes it easier to track and investigate any suspicious activities within the file system.
- Compliance with Security Standards: In many industries, regulatory standards require the use of multi-factor authentication as part of data protection measures. Enabling 2FA helps ensure compliance with these standards and safeguards your organization’s reputation.
In conclusion, enabling two-factor authentication is a simple yet powerful step in bolstering file system security protocols. By implementing this additional layer of verification, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and protect your valuable data from potential breaches. Take advantage of this robust security feature offered by many platforms and applications to enhance the overall security posture of your file system.
Regularly update software
Regularly Update Software: A Crucial Step in File System Security
When it comes to file system security protocols, one simple yet critical tip stands out: regularly update your software. Keeping your file system software up to date is an essential step in maintaining the security and integrity of your data. In this article, we will explore why software updates are important and how they contribute to a robust file system security strategy.
Software updates, also known as patches or fixes, are released by vendors to address vulnerabilities, bugs, or other weaknesses that may exist in their software. By regularly updating your file system software, you ensure that you have the latest security enhancements and bug fixes installed. Here’s why this practice is so crucial:
- Patching Vulnerabilities: Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics to exploit weaknesses in software systems. Software updates often contain patches that address known vulnerabilities, making it harder for attackers to exploit them. Failing to update leaves your file system exposed to potential threats.
- Improved Security Features: Software updates not only fix vulnerabilities but also introduce new security features and enhancements. These updates may include stronger encryption algorithms, improved access controls, or enhanced logging capabilities that help fortify your file system against emerging threats.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries have specific regulatory requirements regarding data security and privacy. Regularly updating your software ensures that you meet these compliance standards and avoid potential penalties or legal consequences.
- Bug Fixes and Stability: Software updates not only address security issues but also fix bugs and improve stability. Unresolved bugs can lead to unexpected crashes or data corruption, compromising the availability and reliability of your file system.
To ensure effective implementation of this tip on regular software updates, consider the following best practices:
– Enable automatic updates whenever possible so that critical patches are installed promptly.
– Regularly check for available updates from trusted sources such as official vendor websites.
– Test updates in a controlled environment before deploying them to production systems to ensure compatibility and minimize any potential disruptions.
– Maintain a comprehensive inventory of all software used in your file system, including third-party applications, and regularly check for updates from their respective vendors.
Remember, file system security is an ongoing effort. By making regular software updates a priority, you strengthen the overall security posture of your file system, reduce vulnerabilities, and protect your valuable data from potential threats. Stay proactive, stay updated!
Monitor activity
When it comes to file system security protocols, one crucial tip that should not be overlooked is the importance of monitoring activity. Monitoring user activity within a file system can provide valuable insights and early detection of any suspicious or unauthorized actions.
By implementing robust monitoring tools, administrators can keep a close eye on file accesses, modifications, deletions, and other critical events. This allows them to identify any unusual patterns or behaviors that may indicate a security breach or potential threat.
Monitoring activity serves multiple purposes in enhancing file system security. Firstly, it helps detect any unauthorized access attempts. By closely monitoring login attempts and tracking user activities, administrators can quickly identify if someone is trying to gain unauthorized access to sensitive files or directories.
Secondly, monitoring activity aids in identifying insider threats. Unfortunately, not all security breaches come from external sources. Employees or authorized users with malicious intent may attempt to misuse their privileges or access confidential information without proper authorization. By closely monitoring user activities, organizations can detect and mitigate such insider threats before they cause significant damage.
Additionally, activity monitoring assists in compliance with regulatory requirements. Many industries have specific data protection regulations that require organizations to maintain audit trails and demonstrate accountability for their data handling practices. By implementing robust monitoring systems, organizations can ensure they have the necessary records to meet compliance standards.
To effectively monitor activity within a file system, organizations should consider implementing intrusion detection systems (IDS) or intrusion prevention systems (IPS). These tools actively monitor network traffic and file accesses for any signs of suspicious behavior or unauthorized access attempts.
In conclusion, monitoring activity within a file system is a critical aspect of maintaining robust security protocols. By closely tracking user activities and network traffic, organizations can detect and respond swiftly to potential security breaches or insider threats. Implementing appropriate monitoring tools and regularly reviewing logs can significantly enhance the overall security posture of your file system infrastructure.
Backup frequently
The importance of backing up your files cannot be overstated when it comes to file system security protocols. Regularly creating backups of your data is a simple yet powerful practice that can save you from potential disasters and ensure the safety of your valuable information.
File systems are not immune to issues like hardware failures, software glitches, malware attacks, or even human errors. Any of these incidents can lead to data loss or corruption, causing significant disruptions to your operations. This is where backups come to the rescue.
By backing up your files frequently, you create an additional layer of protection against these unforeseen events. In the event of a system failure or data breach, having a recent backup allows you to restore your files and resume normal operations quickly. It acts as an insurance policy for your data.
When creating backups, consider the following best practices:
- Regularity: Set up a backup schedule that suits your needs and the criticality of your data. Depending on how frequently your files change, daily or weekly backups may be appropriate. The more often you back up, the less data you stand to lose in case of an incident.
- Redundancy: Maintain multiple copies of your backups in different locations or storage mediums. This ensures that if one backup becomes inaccessible or corrupted, you have alternative options available.
- Verification: After each backup operation, verify the integrity and completeness of the backed-up data. Performing periodic checks helps ensure that your backups are reliable and can be restored successfully when needed.
- Automation: Use automated backup solutions whenever possible to streamline the process and reduce the chance of human error or forgetfulness.
- Offsite Storage: Consider storing at least one copy of your backups offsite or in a separate physical location from where your primary files reside. This protects against physical damage or theft that could affect both primary files and local backups.
Remember that backups are not a one-time task; they require ongoing attention and maintenance. As your data grows and changes, adjust your backup strategy accordingly to ensure that all critical files are included.
In summary, frequent backups are an essential aspect of file system security protocols. They provide a safety net for your data, allowing you to recover quickly in the face of unexpected events. By following best practices such as regularity, redundancy, verification, automation, and offsite storage, you can protect your valuable information and maintain business continuity. Don’t underestimate the power of backups – they can be a lifesaver when it comes to file system security.
