Database Security: Safeguarding Your Digital Assets
In today’s data-driven world, the security of databases is of utmost importance. With sensitive information stored within these digital vaults, protecting data from unauthorized access, breaches, and malicious activities has become a critical concern for organizations across industries. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of database security and discuss effective strategies to safeguard your valuable digital assets.
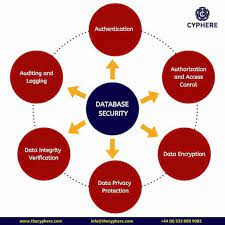
- Access Control: Controlling who can access your database is the first line of defense against potential threats. Implementing robust authentication mechanisms such as strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access control (RBAC) helps ensure that only authorized individuals can interact with the database.
- Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit is vital to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Utilizing strong encryption algorithms and secure key management practices adds an extra layer of protection against potential breaches or data leaks.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Keeping your database software up to date with the latest security patches is crucial in addressing vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Regularly applying patches and updates provided by the database vendors helps protect against known vulnerabilities and ensures that your system remains resilient.
- Database Auditing and Monitoring: Implementing robust auditing mechanisms allows you to track user activities within the database environment. By monitoring logs and analyzing audit trails, you can identify any suspicious or anomalous behavior promptly, enabling timely response to potential security incidents.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Having a comprehensive backup strategy in place mitigates the impact of potential data loss or corruption due to security incidents or system failures. Regularly backing up your databases and ensuring that backups are securely stored offsite provides a safety net for recovering critical data when needed.
- Secure Network Configuration: Securing the network infrastructure surrounding your databases is essential for preventing unauthorized access. Implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), virtual private networks (VPNs), and secure network protocols ensures that data is transmitted securely and protects against external threats.
- Database Activity Monitoring: Deploying database activity monitoring tools enables real-time tracking and analysis of database events. This helps detect suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or abnormal data modifications, allowing for immediate response to potential security breaches.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Human error is often a significant factor in security breaches. Providing regular training sessions to employees on best practices for database security, including password hygiene, social engineering awareness, and safe data handling practices, can significantly reduce the risk of accidental data exposure or unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conducting periodic security assessments and penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your database infrastructure. By proactively identifying potential risks, you can take appropriate measures to address them before they are exploited by malicious actors.
- Compliance with Regulations: Depending on your industry, you may be subject to specific regulatory requirements regarding the protection of sensitive data. Ensuring compliance with relevant regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS not only helps protect your organization from legal consequences but also enhances overall data security practices.
In conclusion, database security is an ongoing process that requires a multi-layered approach to protect valuable digital assets from evolving threats. By implementing robust access controls, encryption mechanisms, regular patching, monitoring tools, employee training programs, and complying with regulations, organizations can significantly enhance their database security posture. Prioritizing the protection of databases is essential for maintaining trust with customers and stakeholders while safeguarding sensitive information in an increasingly interconnected world.
Commonly Asked Questions About Database Security: Types, Measures, and Layers
- What are the 5 types of database security?
- How do you secure your database?
- What do you mean by database security?
- What are the three layers of database security?
What are the 5 types of database security?
There are several types of database security measures that organizations commonly employ to protect their databases. Here are five key types:
- Access Control: Access control ensures that only authorized individuals or entities can access the database. This involves implementing authentication mechanisms, such as usernames and passwords, and employing techniques like role-based access control (RBAC) to assign specific permissions and privileges to different users based on their roles or responsibilities.
- Encryption: Encryption is the process of converting data into a secure form that can only be accessed with an encryption key. Database encryption involves encrypting data at rest (stored on disk) and in transit (during transmission over networks). By encrypting sensitive information, even if it falls into the wrong hands, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Auditing and monitoring involve keeping track of database activities and events to detect any suspicious or unauthorized actions. This includes monitoring user logins, tracking changes made to the database, analyzing access patterns, and generating audit logs for review. By regularly reviewing these logs, organizations can identify potential security breaches or anomalies quickly.
- Backup and Recovery: Database backup and recovery strategies are crucial for ensuring data availability and protecting against data loss due to security incidents or system failures. Regularly backing up databases allows organizations to restore data in case of accidental deletion, corruption, or ransomware attacks.
- Security Assessments: Conducting regular security assessments helps identify vulnerabilities in the database infrastructure that could be exploited by attackers. These assessments can include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, code reviews, and risk assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of existing security controls and identify areas for improvement.
It’s important to note that these five types of database security measures often work together as part of a comprehensive security strategy rather than being standalone solutions. Implementing multiple layers of security helps mitigate risks effectively and provides a stronger defense against potential threats to databases.
How do you secure your database?
Securing a database involves implementing multiple layers of protection to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data. Here are some essential steps you can take to secure your database:
- Strong Authentication: Implement robust authentication mechanisms such as strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA), or biometric authentication to ensure that only authorized users can access the database.
- Access Control: Utilize role-based access control (RBAC) to grant appropriate privileges to users based on their roles and responsibilities. Restrict access privileges to the minimum necessary level required for users to perform their tasks.
- Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. Utilize strong encryption algorithms and secure key management practices to safeguard data from potential breaches or leaks.
- Regular Patching and Updates: Keep your database software up to date with the latest security patches provided by the vendor. Regularly applying patches helps address known vulnerabilities and protect against potential exploits.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Enable auditing features within your database system to track user activities, monitor for suspicious behavior, and generate audit logs. Regularly review these logs for any anomalies or signs of unauthorized access attempts.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Establish a comprehensive backup strategy that includes regular backups of your databases. Store backups securely offsite or in encrypted formats to mitigate the impact of potential data loss or corruption due to security incidents or system failures.
- Secure Network Configuration: Configure firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), virtual private networks (VPNs), and secure network protocols to protect your database from external threats. Restrict network access only to authorized users or systems.
- Database Activity Monitoring: Deploy database activity monitoring tools that can provide real-time alerts for suspicious activities such as abnormal data modifications or unauthorized access attempts.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees on best practices for database security, including password hygiene, social engineering awareness, and safe data handling practices. Regular training sessions help reduce the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conduct periodic security assessments, vulnerability scans, and penetration testing to identify potential weaknesses in your database infrastructure. Address any identified vulnerabilities promptly to maintain a strong security posture.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure compliance with relevant industry regulations and data protection laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS if applicable to your organization. Implement necessary controls and processes to meet the requirements and protect sensitive data.
Remember that database security is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, updates, and adaptation to address emerging threats. It is essential to stay informed about the latest security practices and technologies to keep your databases protected against evolving risks.
What do you mean by database security?
Database security refers to the measures and practices implemented to protect databases from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. It involves safeguarding the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data stored within a database system.
Database security aims to ensure that only authorized individuals or entities can access and manipulate the data while preventing unauthorized users from gaining entry or tampering with sensitive information. It encompasses various aspects such as access control, encryption, auditing, monitoring, backup and recovery procedures, network security configurations, employee training, and compliance with relevant regulations.
The goal of database security is to minimize the risk of data loss, unauthorized disclosure or modification of information, and disruptions to business operations caused by security incidents. By implementing robust security measures and best practices, organizations can protect their valuable digital assets stored within databases from potential threats posed by hackers, insiders with malicious intent, or accidental mistakes.
What are the three layers of database security?
The three layers of database security are:
- Physical Security: This layer focuses on protecting the physical infrastructure that houses the database servers and storage devices. It includes measures such as secure data centers with restricted access, surveillance systems, environmental controls (e.g., temperature and humidity), and backup power supplies to ensure continuous operation and prevent unauthorized physical access or damage to the hardware.
- Network Security: This layer involves securing the network infrastructure that connects the database servers to other systems and users. It includes measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), virtual private networks (VPNs), secure network protocols (e.g., SSL/TLS), and strong authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access, eavesdropping, or tampering with data during transmission.
- Data Security: This layer focuses on protecting the actual data stored within the database. It includes measures such as access controls, encryption, auditing, and monitoring. Access controls ensure that only authorized users have appropriate privileges to access or modify specific data. Encryption techniques protect data at rest (stored on disks) and in transit (during communication). Auditing tracks user activities within the database environment for monitoring and detecting suspicious behavior or security breaches.
These three layers work together to provide a comprehensive approach to database security, addressing physical vulnerabilities, protecting network communications, and safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access or manipulation. By implementing security measures across these layers, organizations can establish a strong defense against potential threats to their valuable databases.
