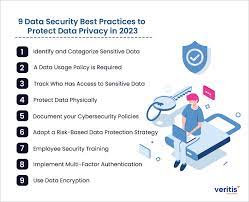
Data Security Best Practices: Safeguarding Your Digital Assets
In today’s digital age, data security has become a paramount concern for individuals and organizations alike. With the ever-increasing volume of sensitive information being stored and transmitted online, it is crucial to implement robust data security measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. In this article, we will explore some essential data security best practices that can help safeguard your valuable digital assets.
- Strong Passwords: The first line of defense in data security is having strong, unique passwords for all your accounts. Avoid common passwords like “123456” or “password” and opt for complex combinations of letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and symbols. Additionally, consider using a password manager to securely store and generate strong passwords.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible. MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide additional verification factors such as a fingerprint or a one-time passcode sent to their mobile device. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep your operating systems, applications, and antivirus software up to date with the latest patches and updates. Software vendors often release updates that address newly discovered vulnerabilities or weaknesses in their products. By staying updated, you can protect yourself against known exploits used by hackers.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it falls into the wrong hands, it remains unreadable without the encryption key. Utilize encryption technologies such as SSL/TLS for securing communications over networks and file-level encryption for protecting files at rest.
- Secure Network Connections: When accessing sensitive information or conducting transactions online, make sure you are connected to secure networks only. Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks that are unencrypted or shared with unknown entities as they pose significant risks of eavesdropping or man-in-the-middle attacks. Consider using a virtual private network (VPN) for an added layer of security.
- Regular Data Backups: Implement a robust data backup strategy to ensure that your valuable information is protected against accidental deletion, hardware failures, or ransomware attacks. Regularly backup your data to offline or cloud storage solutions, and test the restoration process periodically to verify data integrity.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Human error remains one of the most significant vulnerabilities in data security. Educate employees about best practices such as recognizing phishing attempts, avoiding suspicious links or attachments, and practicing good password hygiene. Regularly conduct training sessions and keep employees informed about emerging threats.
- Access Control and Least Privilege: Limit user access rights to only what is necessary for their roles and responsibilities. Implement the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users have access only to the specific resources required to perform their tasks effectively. Regularly review user permissions and revoke unnecessary privileges promptly.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to be taken in case of a security breach or data incident. This plan should include procedures for containment, investigation, recovery, and communication with stakeholders. Regularly test and update the plan based on lessons learned from simulated incidents.
- Continuous Monitoring and Auditing: Establish a system for monitoring network activity, user behavior, and system logs to detect any anomalies or potential security breaches promptly. Conduct regular audits to assess compliance with security policies and identify areas for improvement.
By implementing these data security best practices, you can significantly enhance your defenses against cyber threats and safeguard your valuable digital assets. Remember that data security is an ongoing effort that requires vigilance, regular updates, and adaptability to stay ahead of evolving threats in today’s dynamic digital landscape.
Understanding Data Security Best Practices: FAQs on Methods, Types, Principles, and Elements
- What are the 4 ways of securing data?
- What are the 3 types of data security?
- What are the 3 principles of data security?
- What are the four 4 elements of data security?
What are the 4 ways of securing data?
There are several ways to secure data, but here are four fundamental methods:
- Encryption: Encryption is the process of converting data into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms. This ensures that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they cannot understand or use it without the encryption key. Encryption can be applied to data at rest (stored on devices or servers) and data in transit (being transmitted over networks).
- Access Control: Access control involves implementing measures to restrict and manage who can access certain data or resources. It includes techniques such as user authentication (e.g., passwords, biometrics), authorization (assigning specific privileges based on roles or responsibilities), and auditing user activity to track and monitor access.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regularly backing up important data and having a robust disaster recovery plan is crucial for securing data against accidental deletion, hardware failures, natural disasters, or malicious attacks. Backups should be stored securely either offline or in remote locations to prevent loss.
- Security Awareness and Training: Human error remains a significant vulnerability in data security. Educating employees about best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, avoiding suspicious links or attachments, and practicing good password hygiene, is essential. Regular training sessions and awareness programs help foster a security-conscious culture within an organization.
It’s important to note that these methods are not standalone solutions but rather work together in a layered approach to provide comprehensive data security. Organizations must consider implementing multiple security measures tailored to their specific needs and risks to effectively protect their valuable information assets.
What are the 3 types of data security?
The three main types of data security are:
- Physical Security: Physical security focuses on protecting data through physical means. This includes securing servers, data centers, and other physical infrastructure that house sensitive information. Measures such as access controls, video surveillance, and alarm systems are implemented to prevent unauthorized physical access to data storage facilities.
- Technical Security: Technical security involves the use of technological measures to protect data from unauthorized access or manipulation. This includes encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus software, and secure network protocols. Technical security measures aim to safeguard data during transmission over networks and while at rest on storage devices.
- Administrative Security: Administrative security encompasses policies, procedures, and practices that govern the management of data security within an organization. This includes defining user access privileges, implementing authentication mechanisms, conducting regular security audits and assessments, training employees on best practices, and establishing incident response plans. Administrative security ensures that proper protocols are in place to protect data and respond effectively in case of a breach or incident.
These three types of data security work together to create a comprehensive approach to safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. Implementing all three types is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data in today’s digital landscape.
What are the 3 principles of data security?
The three principles of data security are:
- Confidentiality: Confidentiality ensures that only authorized individuals or systems can access and view sensitive information. It involves protecting data from unauthorized disclosure, preventing unauthorized access, and maintaining privacy. Measures such as encryption, access controls, and secure communication channels are implemented to maintain confidentiality.
- Integrity: Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and unaltered throughout its lifecycle. It involves protecting data from unauthorized modification, deletion, or corruption. Data integrity measures include implementing checksums or hash functions to detect any changes in data, using write-protected media or file permissions to prevent unauthorized modifications, and implementing backup and recovery processes to restore data in case of accidental loss or corruption.
- Availability: Availability ensures that authorized users have timely and uninterrupted access to the information they need. It involves ensuring that systems are operational, networks are accessible, and data is available when required. Availability measures include implementing redundant systems for high availability, performing regular backups to prevent data loss, implementing disaster recovery plans to quickly restore services in case of disruptions, and monitoring system performance to identify potential bottlenecks or issues affecting availability.
By adhering to these three principles of data security – confidentiality, integrity, and availability – organizations can establish a strong foundation for protecting their sensitive information from unauthorized access, manipulation, or loss while ensuring its accessibility for authorized users when needed.
What are the four 4 elements of data security?
The four elements of data security are:
- Confidentiality: Confidentiality ensures that data is accessible only to authorized individuals or entities. It involves protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, or interception. Measures such as encryption, access controls, and secure communication channels help maintain confidentiality.
- Integrity: Integrity ensures that data remains accurate, complete, and unaltered throughout its lifecycle. It involves preventing unauthorized modifications, deletions, or tampering with data. Techniques like checksums, digital signatures, and access controls help maintain data integrity.
- Availability: Availability ensures that data is accessible and usable by authorized users when needed. It involves preventing disruptions or outages that could result in the unavailability of critical data. Measures such as redundant systems, backups, disaster recovery plans, and robust network infrastructure help maintain availability.
- Authentication: Authentication verifies the identity of users or entities attempting to access data or systems. It involves validating credentials such as usernames and passwords, biometrics (fingerprint or face recognition), tokens (smart cards), or other authentication factors to ensure that only authorized individuals gain access.
These four elements work together to establish a comprehensive framework for data security. By addressing confidentiality, integrity, availability, and authentication in a holistic manner, organizations can protect their sensitive information from unauthorized access, manipulation, loss, or unauthorized disclosure.
