The Basics of File Systems
A file system is a crucial component of any operating system that manages how data is stored, organized, and accessed on storage devices such as hard drives and SSDs. It provides a structured way to store and retrieve files, ensuring efficient data management and access.
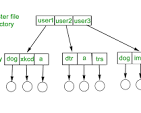
File systems use a hierarchical structure of directories (folders) and files to organize data. Each file is identified by a unique name and location within the file system. The file system also keeps track of metadata associated with each file, such as its size, creation date, and permissions.
One key function of a file system is to allocate storage space for files on the storage device. It manages disk space by dividing it into clusters or blocks that can be allocated to store individual files. This allocation process helps optimize storage efficiency and performance.
File systems also provide mechanisms for data protection and recovery. They often include features such as journaling, which logs changes to the file system to ensure data integrity in case of unexpected shutdowns or errors. Backup and recovery tools are also commonly used to safeguard against data loss.
There are various types of file systems designed for different purposes and operating systems. Common examples include FAT32, NTFS, exFAT for Windows systems, HFS+ for macOS, and ext4 for Linux. Each file system has its own characteristics, performance capabilities, and limitations.
In conclusion, understanding the fundamentals of file systems is essential for effective data management and storage. By grasping how file systems work and their role in organizing data, users can make informed decisions about storage solutions and optimize their computing experience.
Understanding File Systems: Definitions, Examples, and How to Check System Files
- What is meant by file system?
- What is an example of a file system?
- How do I check my system files?
- What is the system file?
What is meant by file system?
A file system refers to the structure and organization that an operating system uses to store, manage, and retrieve data on storage devices such as hard drives and SSDs. It defines how files are named, stored, and accessed within a hierarchical directory structure. The file system also manages metadata associated with each file, including attributes like file size, permissions, and timestamps. Essentially, the file system acts as a bridge between the user and the physical storage media, providing a standardized way to interact with data stored on a computer system. Understanding the concept of a file system is fundamental to effectively managing data and ensuring efficient access to files on computing devices.
What is an example of a file system?
An example of a file system is NTFS (New Technology File System), which is commonly used in Windows operating systems. NTFS offers advanced features such as support for large file sizes, file compression, encryption, and access control mechanisms. It provides robust data protection and recovery capabilities, making it a popular choice for storing and managing files on Windows-based computers.
How do I check my system files?
Checking system files is a fundamental task to ensure the stability and integrity of your operating system. To check your system files, you can use built-in tools like System File Checker (SFC) on Windows or Terminal commands on Unix-based systems. These tools scan your system for any corrupted or missing files and attempt to repair them to maintain the overall health of your operating system. Regularly checking system files can help prevent issues that may arise from file corruption, ensuring smooth operation and optimal performance of your computer.
What is the system file?
The frequently asked question “What is the system file?” refers to a crucial component of an operating system that contains essential information and settings required for the system to function properly. The system file, often referred to as system files or system software, includes critical files such as device drivers, configuration files, and libraries that facilitate the interaction between hardware and software components of a computer. These files are integral to the operating system’s operation and play a vital role in managing system resources, executing tasks, and maintaining stability and security. Understanding the significance of system files is key to troubleshooting issues, optimizing performance, and ensuring the overall health of a computer system.
